Fire & Smoke Damper Requirements as per IBC
According to the International Building Code (IBC), fire and smoke dampers are required in certain locations to prevent the spread of smoke and protect people and buildings from fire.
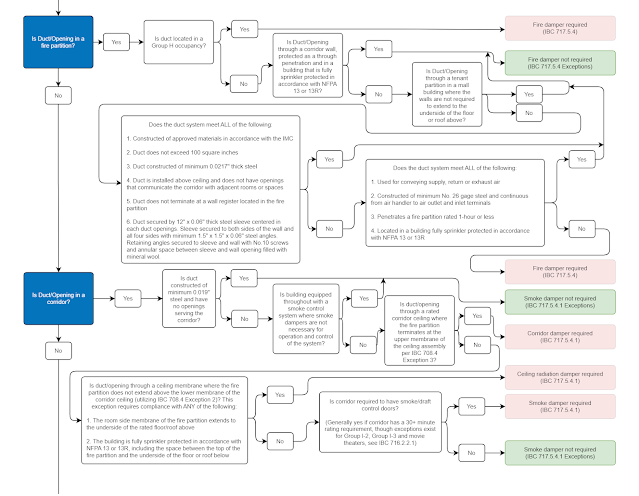
Fire dampers are installed in ducts passing through or in air outlet openings terminating at shaft walls, fire barriers (such as an occupancy separation wall, horizontal exit walls, corridor walls, corridor ceilings, floor-ceiling assemblies) and other fire resistance–rated assemblies as required by a building or life safety code and other applicable standards. Under severe fire exposure, a duct may eventually collapse or significantly deform, creating an opening in the fire barrier. Fire dampers provide a method of protecting such penetrations and openings. Fire dampers must be inspected one year after installation and every four years after that. Hospitals are an exception, and must be inspected after one year and every six years.
Smoke damper’s primary function is to control the movement of smoke in dynamic air distribution systems, and they reduce the possibility of smoke transfer within ductwork or through wall openings. They are installed in ducts passing through, or air outlet openings terminating at, smoke barriers, shaft walls, horizontal exit walls, corridor walls, corridor ceilings, and other barriers designed to resist the spread of smoke as required by a building or life safety code and other applicable standards. Smoke dampers operate automatically on detection of smoke and must function so that smoke movement through the duct is halted. Their activation can be by area detectors that are installed in the related smoke compartment or by detectors that are installed in the air duct systems.




We Have best electrical contractors in lower mainland.Our experience and quality of work represent who we are our and that’s the reason we have represented clients for different projects in our work. Our crew is highly skilled and professional to understand customer needs. Also, we come up with a budget that’s reasonable for the customer and can get the best work out of it. Our company is fully licensed and bonded and all our crew is insured and WCB covered. Fourteen Electrical Ltd. It is a crew of certified electricians that provide customers with all over Lower Mainland and Fraser Valley area.
ReplyDeletelower mainland electrician
Best electrician in Surrey
Certified electricians
rewiring services in lower mainland
best electrical wiring contractor lower mainland
wiring service lower mainland
electrical wiring services lower mainland
best electrical services surrey
electrical services in surrey
best electrical services lower mainland
electrician services lower mainland
best electrical contractors in surrey
Commercial wiring services lower mainland
commercial security system installation lower mainland
residential electrician surrey bc
Ensure your family's safety with reliable residential alarm installation lower mainland, designed to deter intrusions effectively.
ReplyDelete