NFPA 22 Water Tanks for Private Fire Protection – A short Note
In cases
in which the municipal water supply is not available, reliable, or it cannot
provide adequate flow for the fire pump, a fire pump and water storage tank
needs to be used. This is because a fire pump alone can only increase the water
pressure; it cannot increase the flow available. Water storage tanks and pumps
are usually seen in facilities with systems that have a significant water
supply demand, such as large warehouses. Water storage tanks can be made of
various materials such as wood, steel, concrete, fiberglass-reinforced plastic
(FRP), and rubberized fabric.
NFPA 22, Standard for Water Tanks for Private Fire Protection, provides the minimum requirements for the design, construction, installation, and maintenance of tanks and accessory equipment that supply water for private fire protection.
|
Core Chapters |
Chapter 1 |
Introduction |
|
Chapter 2 |
Referenced Publication |
|
|
Chapter 3 |
Definitions |
|
|
Chapter 4 |
General Information |
|
|
Types of Tanks |
Chapter 5 |
Welded Carbon Steel and Composite Concrete and Carbon Steel Gravity
Tanks and Suction Tanks |
|
Chapter 6 |
Factory Coated, Bolted Carbon Steel Tanks |
|
|
Chapter 7 |
Pressure Tanks |
|
|
Chapter 8 |
Wood Gravity Tanks and Suction Tanks |
|
|
Chapter 9 |
Embankment Supported Coated Fabric Suction Tanks |
|
|
Chapter 10 |
Concrete Gravity Tanks and Suction Tanks |
|
|
Chapter 11 |
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic Tanks |
|
|
Constructional |
Chapter 12 |
Tank and Tower Foundations in the Ground |
|
Chapter 13 |
Steel Tank Towers |
|
|
Chapter 14 |
Pipe Connections and Fittings |
|
|
Chapter 15 |
Valve Enclosures and Frost
Protection |
|
|
|
Chapter 16 |
Tank Heating |
|
Chapter 17 |
Acceptance Test Requirements |
|
|
Chapter 18 |
ITM of Water tanks |
|
|
Annex A |
Explanatory Material |
|
|
Annex B |
Typical Installations |
|
|
Annex C |
Informational References |
👉NFPA 22, also known as
the National Fire Protection Association Standard for Water Tanks for Private
Fire Protection, is a crucial guideline that outlines the requirements for the
design, construction, installation, and maintenance of water tanks used for
fire protection purposes.
👉Water
tanks play a vital role in providing an adequate and reliable water supply for
firefighting operations, especially in areas where the public water supply may
be limited or unavailable. These tanks are typically installed in commercial or
industrial properties, as well as in residential communities that require
enhanced fire protection measures.
👉Complying
with NFPA 22 ensures that water tanks are built and maintained to the highest
standards, ensuring their effectiveness during emergencies. Some key provisions
of NFPA 22 include specifications for tank materials, capacity, location, and
access for inspections and maintenance.
👉By
adhering to NFPA 22, property owners and fire protection professionals can
ensure that water tanks are designed to withstand extreme conditions, such as
earthquakes or high winds, and maintain their structural integrity over time.
Regular inspections and maintenance, as outlined in the standard, are essential
to guarantee that the tanks remain in optimal condition and ready to serve
their intended purpose.
⭕ Scope of NFPA 22.
➡️
NFPA 22 provides guidelines to ensure that water tanks used for fire protection
are:
✔️
Properly designed for structural integrity.
✔️
Capable of providing adequate water supply for firefighting.
✔️
Installed and maintained according to fire safety standards.
✅
This standard applies to various types of tanks, including steel, concrete, and
fiberglass, used in fire sprinkler systems, standpipes, and hydrant systems.
🔹
What is a Fire Water Tank?
A fire water tank is a dedicated storage tank designed to hold water
exclusively for fire suppression purposes. It supplies water to fire pumps,
which then distribute it through the fire protection system, ensuring quick and
effective firefighting.
⭕ Key Requirements of NFPA 22.
1. Types of Water Storage Tanks
➡️
NFPA 22 classifies fire water tanks into different categories based on their
construction material and design:
🔹
Steel Tanks – Welded or bolted, commonly used due to durability and
cost-effectiveness.
🔹
Concrete Tanks – Suitable for large capacities and underground applications.
🔹
Fiberglass Tanks – Corrosion-resistant and lightweight, used in specific
environments.
🔹
Wood Tanks – Less common, but used in remote areas.
🔹
Bladder Tanks – Flexible storage solutions, mainly for temporary applications.
2. Tank Sizing and Capacity Requirements.
➡️
The tank’s size and capacity depend on the fire protection system it serves.
Factors considered include:
✔️
Type of hazard (low, moderate, or high risk).
✔️
Required fire flow and duration.
✔️
Local fire codes and regulations.
✅
The tank must be large enough to provide sufficient water supply for the
required fire protection duration, typically ranging from 30 to 90 minutes,
based on system demand.
3. Structural and Seismic Design.
➡️
NFPA 22 ensures that tanks are structurally sound to withstand various
environmental conditions. Key design aspects include:
✔️
Wind and seismic load considerations for earthquake-prone regions.
✔️
Proper foundation and anchoring to prevent overturning.
✔️
Corrosion protection measures to extend tank lifespan.
4. Piping and Connections.
➡️
Water tanks must have reliable piping and connections to ensure uninterrupted
water supply. NFPA 22 specifies:
🔹
Inlet and outlet connections for continuous water replenishment.
🔹
Overflow pipes to prevent excessive water pressure.
🔹
Fire department connections (FDC) for external water supply.
🔹
Common Fire Water Tank Materials (NFPA 22 – 4.2)
Fire water tanks must be constructed from durable, non-corrosive materials to
ensure long-term reliability. NFPA 22 outlines the following materials:
✅
Steel Tanks (Section 4.3, 4.4) – Welded or
bolted steel tanks are common due to their strength and durability.
✅
Concrete Tanks (Section 4.5) – Reinforced
concrete tanks offer longevity and resistance to environmental factors.
✅
Fiberglass Tanks (Section 4.9) –
Corrosion-resistant and lightweight, ideal for certain applications.
✅
Wood Tanks (Section 4.8) – Used in specific installations,
often treated for fire and water resistance.
🔹
Key Components of a Fire Water Tank (NFPA 22 – Chapter 14)
✅
Automatic Float Control Valve – Regulates
water levels to maintain tank capacity.
✅
Tank Overflow Outlet – Prevents overfilling by allowing
excess water to drain.
✅
Vortex Plate (Section 14.2.13) – Prevents air
entrainment and ensures smooth suction to the fire pump.
✅
Pipe Well & Fill Supply Line – Ensures proper
water intake and replenishment.
✅
Minimum Clearance (6 in., Section 14.2.13.3)
– NFPA 22 requires a minimum clearance between the suction pipe and the tank
floor to prevent sediment intake.
TYPES OF TANKS USED IN FIREFIGHTING
GRAVITY
TANK
A storage tank
that uses elevation as a source of pressure, which might be capable of providing
the necessary head pressure to operate a fire suppression system or used to provide
water to a fire pump.
SUCTION TANK
A tank that provides water to a fire pump for which a minimal
amount of head pressure is provided.
BREAK TANK
A tank providing suction to a fire pump whose capacity is
less than the fire protection demand (flow rate times flow duration).
PRESSURE TANK
A tank that uses air or some other gas under pressure to expel
its contents.
BLADDERTANK (not the one Bladder tanks used as foam
concentrate tanks installed in Inaccordance with NFPA16 or NFPA11)
A pressure
tank containing air and water separated by a flexible membrane (bladder).
FIREFIGHTING
WATER TANK MATERIAL
A
firefighting tank can be fabricated using one of the following materials:
SIZING
OF FIREFIGHTING WATER TANK
·
A tank shall be sized so that the stored supply plus
reliable automatic refill shall meet the system demand for the design duration.
·
•A break tank shall be sized for a minimum duration
of 15minutes with the fire pump operating at 150percent of rated capacity.
PURPOSE
OF BREAKTANK
SIZING
OF FIREFIGHTING WATER TANK
CALCULATION
OF THE NET CAPACITY OF FIREFIGHTING TANK
FOR
SUCTION TANKS:
the net capacity shall be the number of gallons between the inlet of the overflow and the level of the vortex plate.
FOR
ALL TANKS OTHER THAN SUCTION TANKS:
the net capacity shall be the number of gallons between the inlet of the overflow and the discharge outlet.
FILLING
OF FIREFIGHTING WATER TANK
The water supply shall be capable of filling the minimum
required fire protection volume within the tank in a maximum of 08 hours.
The tank shall be kept filled, and the water level shall never be more than 4in. (102mm) below the designated fire service level.
DISCHARGE
PIPE SIZING OF FIREFIGHTING WATER TANK
The minimum discharge pipe sizing shall be based on the hydraulic demand of the systems attached to the tank but shall not be less than 06inch.
FIREFIGHTING
WATER TANK OVERFLOW
The
over flow pipe shall have a capacity greater than the fill connection but shall
not be less than 03inch. throughout.
The
in let of the over flow pipe shall be located at the top capacity line or high water.
FIREFIGHTING
WATER TANK DRAIN.
A drain pipe of atleast 02inch. That is fitted with a
controlling valve and a 1∕2inch. Drip valve shall be connected to the tank
discharge pipe near its base and on the tank side of all valves.
PRESSURE
TANK SIZING EXAMPLE
A Pressure tank is to be used to provide a 30min water supply
to a system with a hydraulically calculated demand of 140gpm (530L/min) at a pressure
of 118psi (8.14bar). Due to near by component pressure ratings, it is important
that airpressure in the tank not exceed 175psi (12.0bar). To determine the minimum
size tank.
Solution
Solve for A,
A = 0.7
It means proportion of air in the tank is 70%.
We have been given sprinkler demand as 140 GPM for 30
minutes, yielding a water requirement of 4200 gallons (which is going to be in
30% of the tank)
Hence, the Total size of the pressure tank would be 14,000
gallons.
WOOD
GRAVITY TANKS AND SUCTION TANKS
EMBANKMENT-SUPPORTED
COATED FABRIC SUCTION TANKS
CONCRETE
GRAVITY TANKS AND SUCTION TANKS
FRP
TANKS
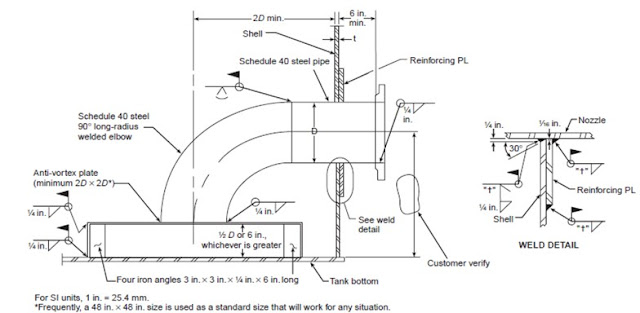
ANTIVORTEX
PLATE
WHEN
TO INSTALL "ANTI-VORTEX PLATE"?:
Where a tank is used as the suction source for a fire pump, the discharge outlet of the tank shall be equipped with an assembly that controls vortex flow.
PURPOSE
OF USING "ANTI-VORTEX PLATE"?
ANTI-VORTEX Plate is installed in the suction line of fire pumps to control the turbulence in flowing water, They are simple in design and very effective in controlling the velocity of the fluid thus preventing cavitation to fire pumps and damage to impellers.
DIMENSIONS
OF "ANTI-VORTEX PLATE"?
The
assembly shall consist of a horizontal steel plate that is at least twice the
diameter of the outlet on anel bow fitting.
Large,
standard size anti-vortex plates [48in.X48in.(1219mm×1219mm)] are most
common and are desirable, as they are adequate for all sizes of fire protection
pump suction pipes normally used
INSTALLATION
DIMENSIONS
Mounted at the outlet a distance above the bottom of the tank
equal to one-half the diameter of the discharge pipe or 152mm which
ever is greater.
ANTI-VORTEX
PLATE INSPECTION
Inspection
of anti-vortex plate shall be after completion of the tank construction,
and before filling the tank with water.
The
inspection shall verify that the horizontal steel plate and long radius elbow are
installed properly and meet the requirements of dimensions and installation height
mentioned above.
✅
Ensures Reliable Water Supply – Provides a
dedicated source of water for firefighting.
✅
NFPA Compliance – Fire tanks must adhere to NFPA 22
standards to guarantee proper operation.
✅
Prevents Water Shortages – Stores sufficient water to meet the
system’s design flow requirements.
✅
Supports Fire Pumps – Ensures pumps receive consistent
water flow without air pockets or cavitation risks.
✅
Works in Remote Areas – Essential for buildings where
municipal water supply is insufficient or unreliable.
🔹
NFPA 22 Fire Water Tank Requirements
🔹
Fire water tanks must be designed based on the building’s fire protection
demand (NFPA 22 – Chapter 4).
🔹
Tanks should have proper inlets, outlets, overflow, and drain systems to
maintain efficiency.
🔹
Anti-vortex plates (Section 14.2.13) must be installed at the suction intake to
prevent turbulence and air pockets.
🔹
Tanks should have minimum clearances to ensure debris and sediment do not enter
the pump suction line.
Inspection, Testing, and Maintenance.
➡️
Regular inspection, testing, and maintenance (ITM) are crucial to keep tanks
operational. NFPA 22 outlines:
✔️
Monthly visual inspections for leaks, corrosion, and sediment buildup.
✔️
Annual structural assessments to check for wear and damage.
✔️
Periodic water quality testing to prevent contamination.
1. NFPA 22
2. 21st edition of the Fire Protection Handbook
3. https://firepiping.com/en/fire-tanks/
4. https://www.beltecno-global.com/blog/fire-fighting-tank
5. https://www.nfpa.org/news-blogs-and-articles/blogs/2024/10/30/nfpa-22-and-water-storage-tanks


















nice article
ReplyDelete